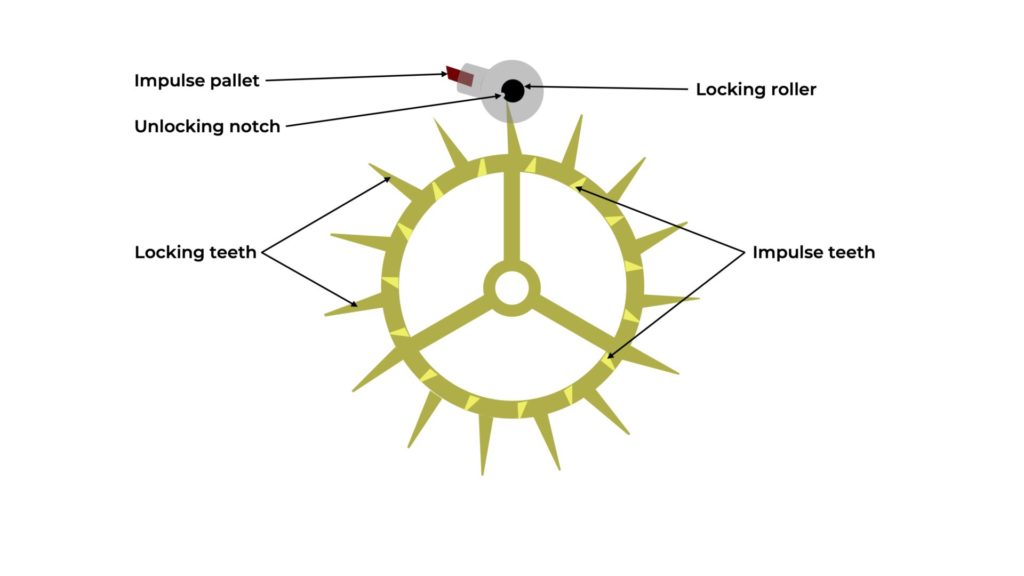
DUPLEX ESCAPEMENT
It is a frictional rest escapement with a single-beat action (or triple-beat lost motion in the duplex-Jacot variant).
The duplex escapement represents a significant milestone in the history of mechanical chronometry. Developed in the 18th century, it embodies an effort to improve the accuracy and regularity of timepieces at a time when precise timekeeping was becoming essential for navigation, science, and social organisation. This type of escapement, both rare and technically refined, served as an intermediate solution between recoil escapements, such as the verge escapement or the crown wheel escapement, and detached escapements, such as the detent escapement or the Swiss lever escapement.
Adapted from a pendulum clock escapement by Jean-Baptiste Dutertre, the duplex escapement reached its final functional design around 1750, thanks to Pierre Le Roy.
It takes its name from the double profile of its escape wheel, which features two distinct sets of teeth, each fulfilling a specific role in the unlocking and impulse phases of energy transmission.
Over the course of a century, the duplex escapement underwent numerous improvements aimed at enhancing precision and lowering production costs, particularly through the stamping of escape wheels. One of the best-known variants, the Duplex-Jacot escapement, was developed by Charles-Edouard Jacot. This version delivers one impulse for every four alternations (i.e. three lost beats). When combined with a balance oscillating at 14,400 A/h (or 4 alternations per second), it enables a deadbeat seconds display without requiring an additional complication.
A contemporary of the cylinder escapement, the duplex escapement enjoyed considerable success before ultimately being superseded by the Swiss lever escapement.
Advantages
The duplex escapement offers several notable advantages:
-
Excellent rate stability of the balance due to the clear separation between the impulse and locking phases.
-
Reduced friction compared to cylinder or verge escapements.
-
Relative mechanical simplicity, with few moving components in interaction.
-
Lower production cost, as the escape wheel could be manufactured by stamping.
These qualities made it particularly well suited to high-precision pocket watches prior to the widespread adoption of the Swiss lever escapement.
Disadvantages
Despite its technical merits, the duplex escapement also presents several limitations:
-
Mechanical fragility, especially in the escape wheel’s double-profile design, whose locking teeth are particularly delicate.
-
Shock sensitivity, making it ill-suited to watches worn in dynamic conditions.
-
Unidirectional impulse, requiring highly accurate adjustment to maintain balanced oscillations of the balance wheel.
These shortcomings contributed to its gradual decline in favour of more reliable, low-friction detached escapements.