DIFFERENT MEASUREMENTS AND THEIR UNITS
Whether dimensional, angular, electrical, optical, or related to time, measurements are essential in watchmaking manufacturing processes. Indeed, they themselves work as instruments capable of compiling numerous measurements. In watchmaking, units of measurement are often adapted and calibrated to the industry’s specific needs.

TIME
Whether indicating time or measuring a defined period – be it long or extremely short – time measurement employs a wide range of units of measurement. Even the dividing the hour can change, becoming a decimal in specific cases. Here, we address the units most commonly encountered in watchmaking.
LENGTH AND ANGLES
Contrary to most industries, the unit of length measurement used in watchmaking is the millimetre. This choice was made due to the limited dimensions of a watch, its components, and the precision they require. Angular measurements are traditionally expressed in degrees and all their subdivisions (angular minutes, angular seconds, etc.).

MASS
Some components must be lightweight, while others are heavy. Some must be balanced, while others need not be. Mass and inertia are values constantly present in watchmaking regardless of production methods or a component’s nature.

TEMPERATURE
In many manufacturing processes, strict temperature control is essential. Temperature and its variations also have a significant impact on the power reserve of a watch (especially a mechanical watch ). Depending on the situation, Celsius, Fahrenheit, or Kelvin units can be used, requiring a high level of precision and advanced measurement technology. In other cases, measurements may be more empirical. For example, the temperature of tempering is evaluated by the eye based on the colours the steel takes on as its temperature rises (e.g., straw yellow = approx. 230°C, dark blue = approx. 288°C).
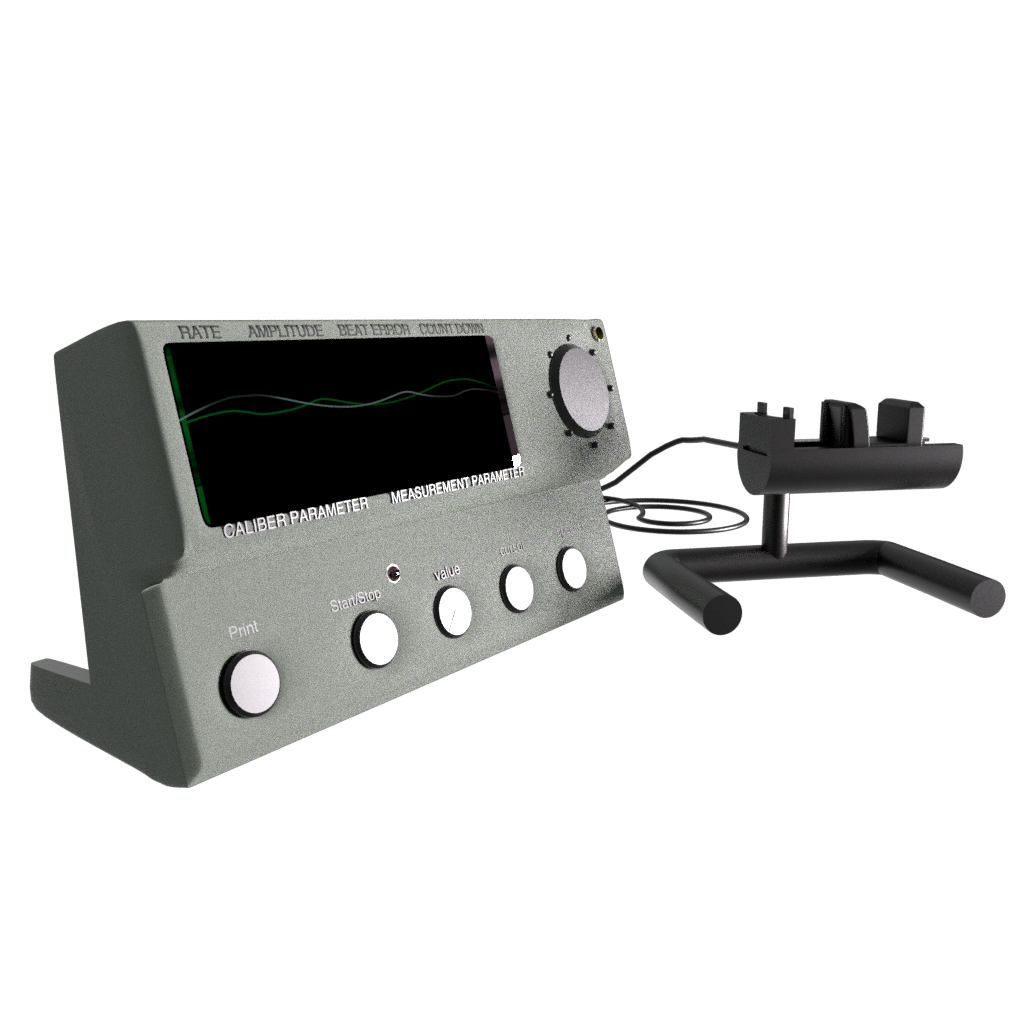

FREQUENCY
This is the number of times a periodic phenomenon repeats within a defined period of time. In watchmaking, the most common frequency measurement is that of the regulating organ (oscillator). This is commonly expressed in two distinct units: the number of alternations per hour (vph or bph) or the number of oscillations per second (Hertz, Hz). For example, 18,000 vph is equal to 2.5 Hz.
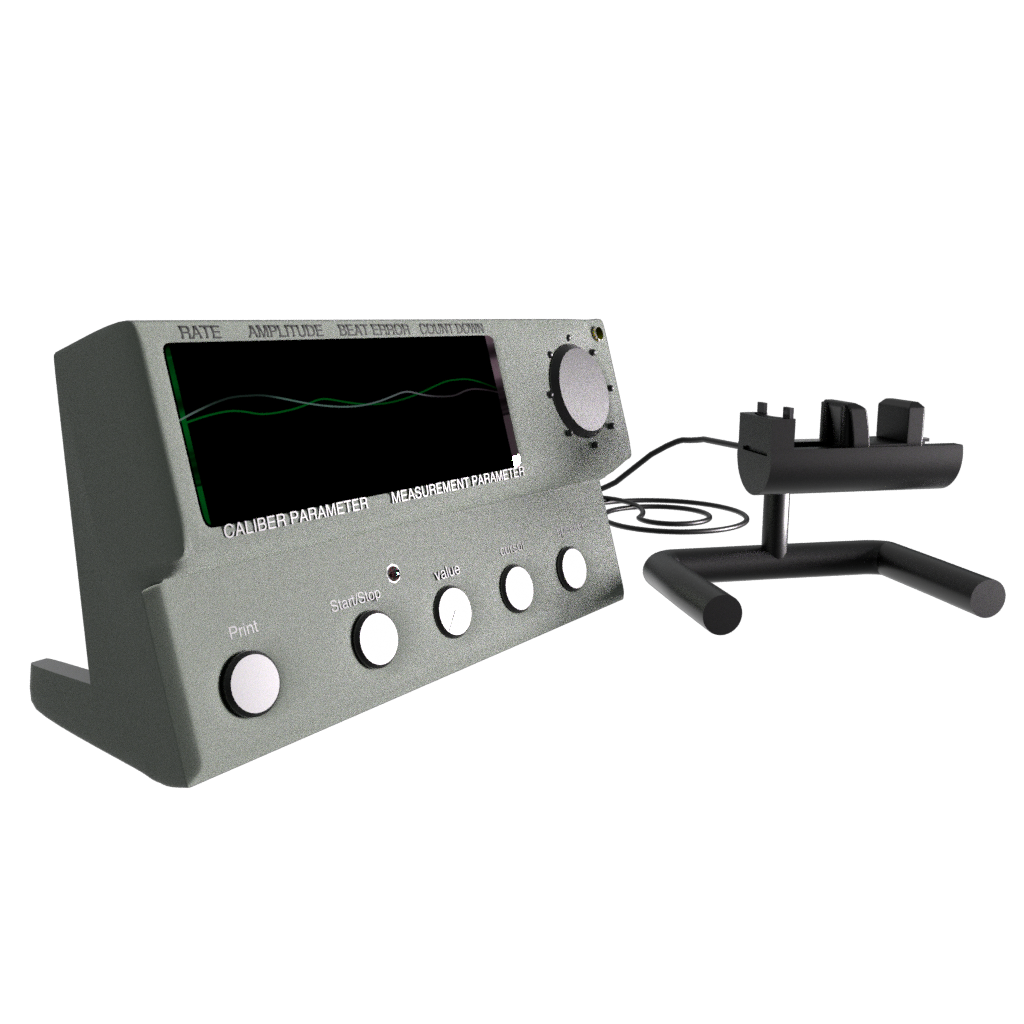

AMPLITUDE
Amplitude expressesthe difference between the extreme values of a quantity (a wave). In watchmaking, a watch’s accuracy depends on the oscillator’s amplitude. It refers to the angle travelled by the balance wheel from one end of its swing to the other. This is expressed in degrees (°).
ELECTRICAL MEASUREMENTS
While there is, by definition, no electrical presence in a mechanical watch, electricity and electronics are present in most time measurement devices. The first electric clocks were produced in the first half of the 19th century. Today, some clocks and watches are occasionally equipped with hybrid movements (electro-mechanical). Electricity powers the workshops, and some machines use electricity as a tool. For example, an electric arc cuts material in electrical discharge machining, welds feet onto the back of a dial or two parts of the tweezers together. And an electric current “carries” material during galvanic treatment. Electrical measurements are thus omnipresent in modern watchmaking, whether artisanal or industrial.

HARDNESS
The hardness of a material determines many characteristics of a component: its resistance to wear, shock, or scratches as well as its friction coefficient . As a rule, a tool must be harder than the material it works on. Hardness is an essential criterion for the functional properties of a component as well as for the means required to manufacture it. Many units of measurement exist and are used, as do many standardized hardness test methods.

LIGHT
Light is present at various manufacturing stages or processes. It is used in chemical etching methods, photolithographic processes (DRIE etching, UV-LIGA), or to set an adhesive or composite lacquer. Optics are mainly applied in checking dimensional measures during production. In relation to the watch itself, optics and light measurements specifically relate to the displays (intensity of a luminescent material, UV resistance, refraction, diffraction, etc.).
BECOME A CONTENT CONTRIBUTOR
HOROPEDIA is a participative knowledge platform and we invite all those who wish to contribute to this adventure of sharing watchmaking knowledge to join us.
It can be additional explanations, images or other illustrations or terms not yet identified that deserve to be.
