ESCAPE WHEEL ASSEMBLY
Figure 1: Plan of an assembled escape wheel
In the gear train of the movement, the escape wheel assembly follows the third wheel. Although the escape wheel assembly is a single, inseparable component, its pinion belongs to the counting and transmission organ (gear train), whereas its wheel forms part of the distribution organ (the escapement).
The Escape Wheel Assembly
Like other wheels, the escape wheel consists of a pinion and a wheel plate.
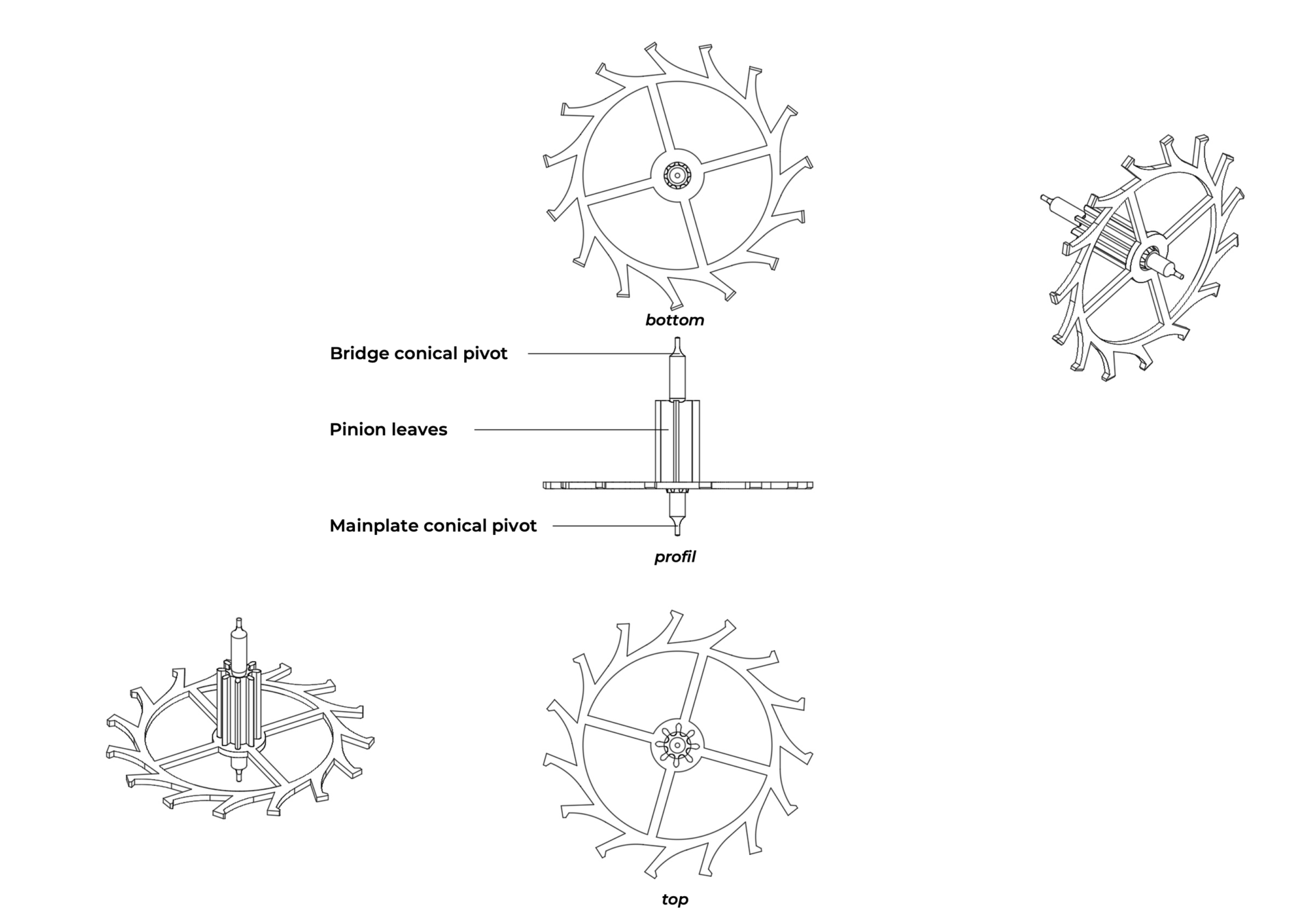
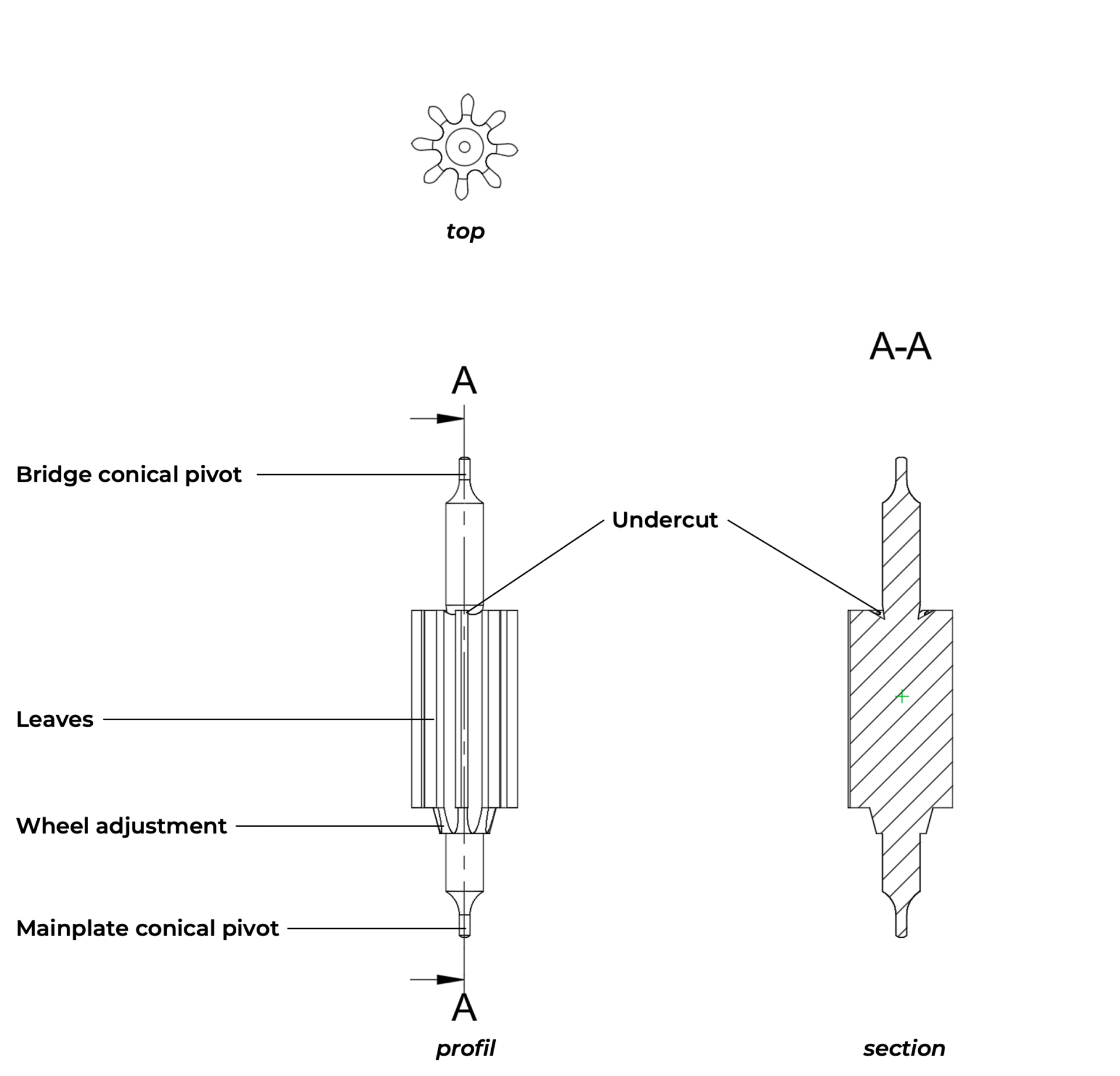
Pinion
The pinion is similar to those of other wheels. It is driven by the third wheel and belongs to the counting and transmission organ (gear train).
Wheel plate
The wheel plate is distinguished by the shape of its toothing and the material from which it is made. Usually of steel, the wheel may also be made of gold, nickel-phosphorus (NiP, by UV-LIGA), or silicon (DRIE), depending on the manufacturing method and the type of escapement. Steel is favoured when the escape wheel transmits its impulse to ruby pallets (as in the Swiss lever escapement). This material pairing optimally reduces friction, which explains the predominance of the Swiss lever escapement in over 99% of modern watches.
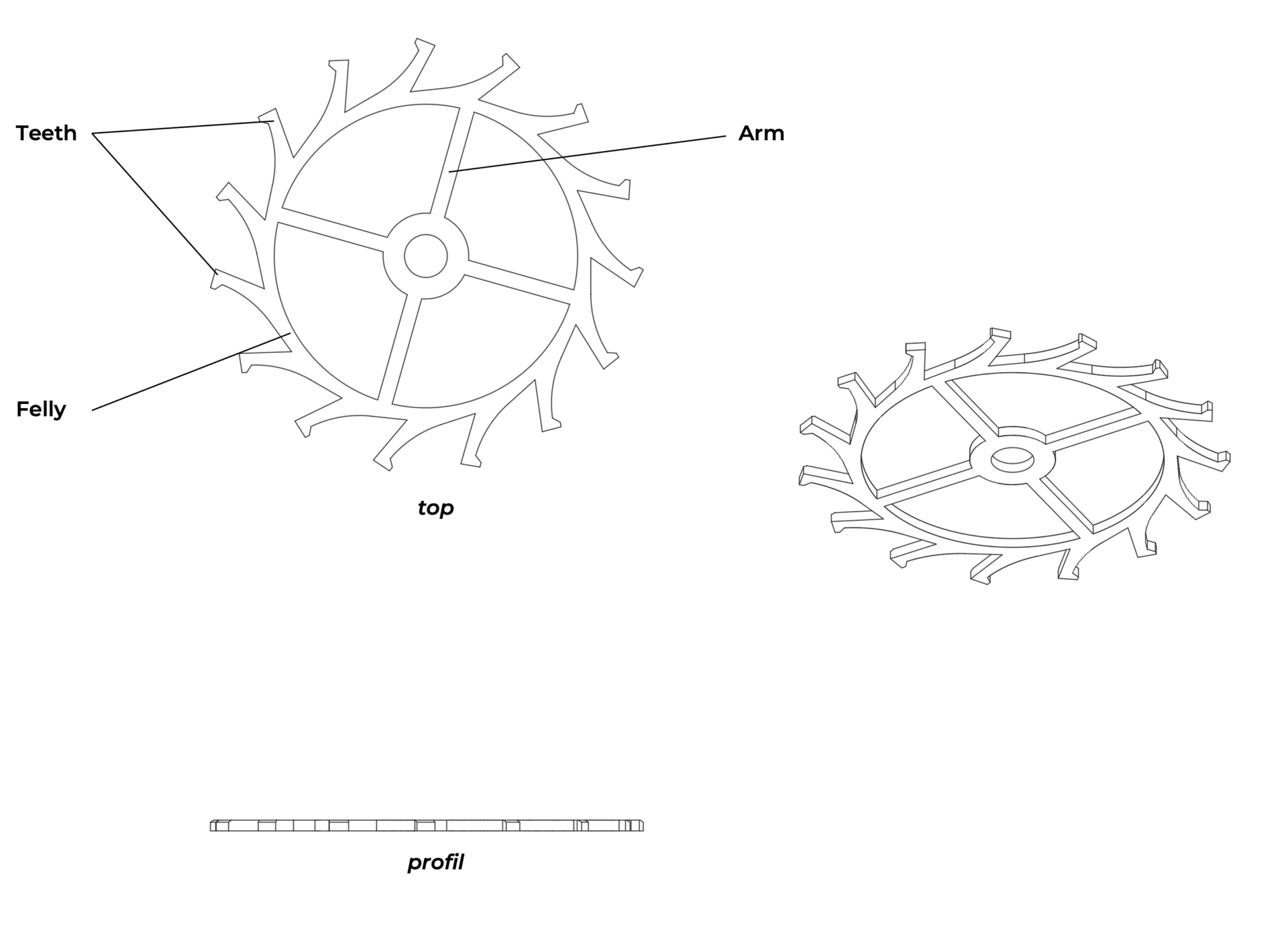
Four-arms geometry
Because of their small size and the rigidity of their material, escape wheels typically have only four arms (compared with five arms for the wheels of the gear train). This reduces weight, lightness being a crucial quality for the escape wheel in particular.
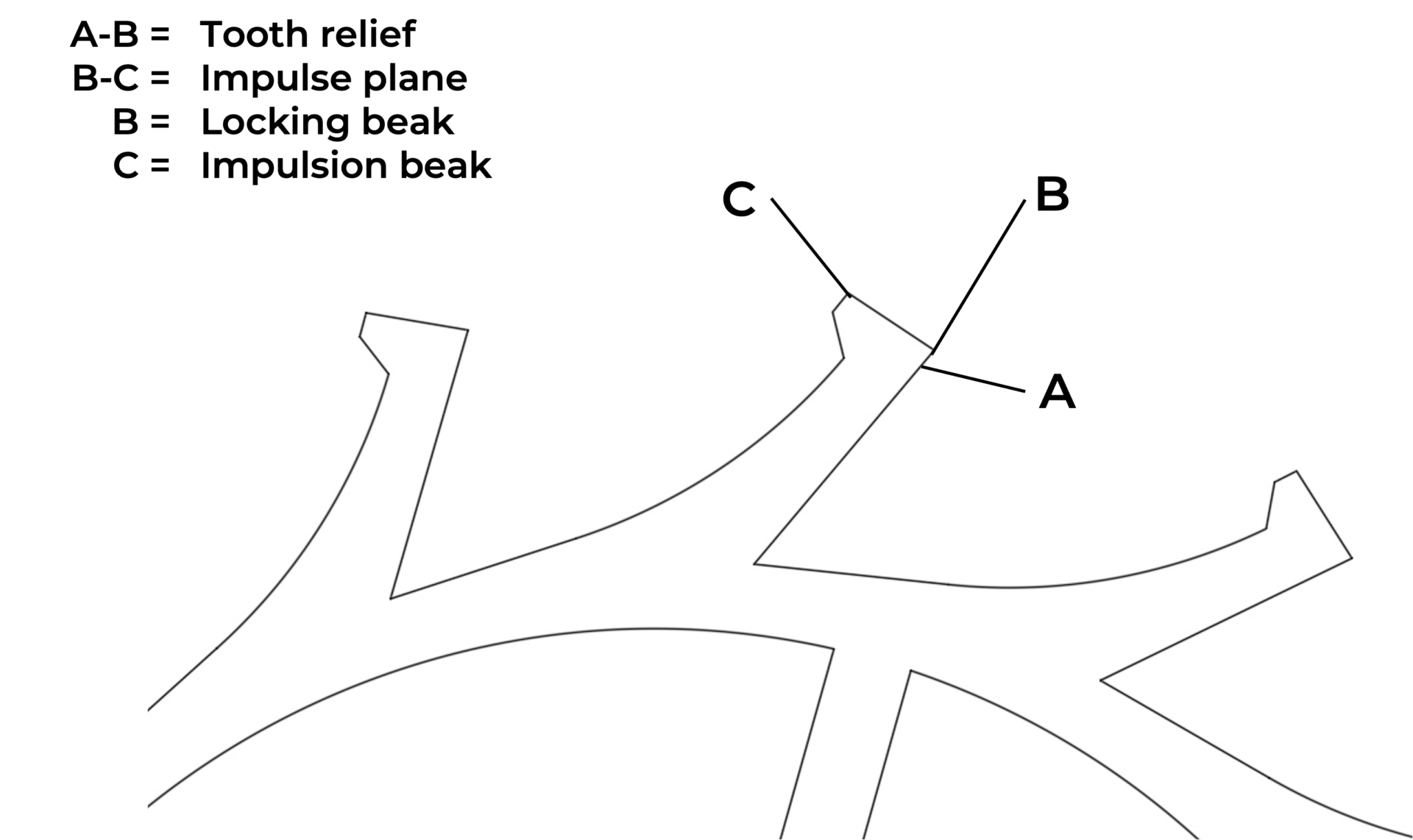
Special toothing
The distinctive toothing of the escape wheel is designed for its special interaction with the lever and its pallets. The lever, the escape wheel, and the double roller together constitute the escapement, which serves a dual purpose: to stop the movement when the balance wheel freely oscillates and to transmit regular impulses to the regulating organ by transforming the rotational movement of the gear train into an oscillatory movement of the regulating organ.
The first escapements appeared in China in the 8th century. They continued to evolve, exhibiting a multitude of diversities, and were the ongoing result of research and studies aimed at improving their performance. The lever was invented by British scientist Robert Hooke in 1657. It initially only regulated clocks and became widespread for its precision and low energy consumption. One of the greatest challenges for watchmakers of the 18th century was finding escapement types capable of functioning in a pocket watch, with minimal influence from the watch’s positions and shocks.
The English watchmakers were the most inventive and prolific in terms of escapements. It was another English watchmaker, Thomas Mudge, who invented… the Swiss lever escapement. This escapement was initially produced for high-end watches before becoming widespread and establishing itself between the late 19th century and the early 20th century, with industrialisation improving its precision and reducing manufacturing costs.
Progress in escapement calculations and the performance of tools and machines allowed, in the late 1960s, an increase in the number of teeth on the escape wheel, achieving higher regulation frequencies (up to 5Hz).
The latest and one of the most significant evolutions arrived at the beginning of the 21st century with the horological application of silicon produced by the photolithographic process. The advantages of this industrial method are numerous: escape wheels no longer require expensive cutters for tooth cutting, the material can be maximally lightweight, and it is non-magnetic.
Depending on the type of escapement, different materials may be used for the fabrication of the escape wheel plate, and the manufacturing operations may differ accordingly. In the case of a Swiss lever escapement, the escape wheel will generally be made of steel. The craftsman will proceed using the same method as for a traditional wheel plate. However, tooth cutting requires the use of up to four different mills. This can be done using a gear-cutting machine or a lathe with a dividing plate. The cost of mills and the numerous operations required for their production make the escape wheel an expensive component to manufacture.
Traditionally, the surfaces of the escape wheel are polished. This finishing prevents the oil, which limits friction between the escape wheel teeth and the lever pallets, from sliding off the flats of the wheel. A surface treatment of the wheel, called epilamation, also helps contain the oil in the tooth profile preventing it from spreading onto the plate surfaces.
Industrially, the escape wheel is turned and machined using an automatic lathe, which can also mill the arms of the plate. Tooth cutting is done on a gear-cutting machine and requires, in this case as well, the use of several mills and many cutting operations.
The material (silicon) and the manufacturing process described here are identical to those used in the production of integrated circuits. Introduced in watchmaking at the very beginning of the 21st century, this method offers numerous advantages.
The principle is to cut (engrave) a silicon plate to a given thickness (generally that of the finished component) using the photolithographic process. This method allows for the realization of the most complex profiles with a precision reaching the micron. Depending on the size of the components to be made, several hundred pieces can be produced simultaneously on the same substrate plate. The most complex profiles can be obtained without the inconvenience of the radii of a milling tool or even the wire of an electrical discharge machine. As this process exerts no mechanical stress, it is possible to produce very thin components (springs, etc.) or pierce them to limit weight, which is particularly beneficial for the escape wheel.
Silicon is a material that is harder than steel, has excellent elasticity, and is non-magnetic. The progress of this technology and its success make it increasingly attractive in terms of production costs and tend to become widespread for the manufacture of many components (especially for the escapement wheels and the regulating organ).